给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
- 展开后的单链表应该同样使用
TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
- 展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
示例 1:
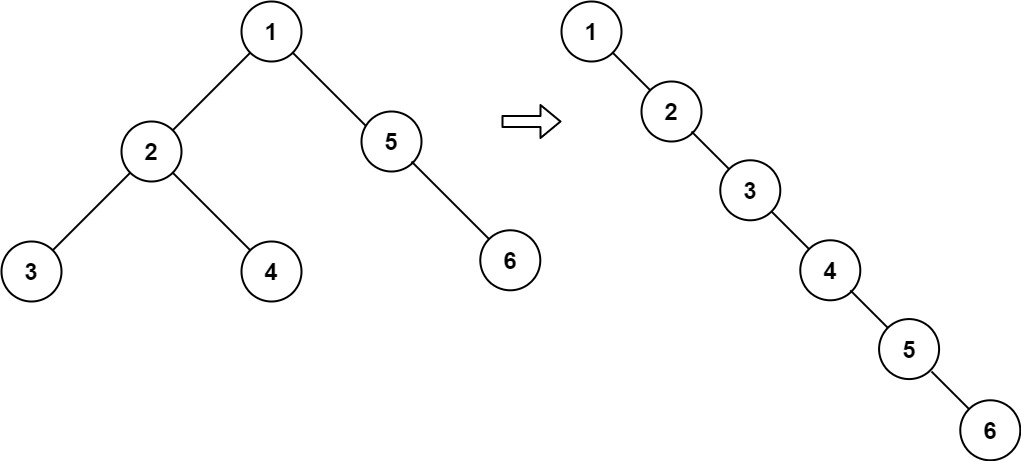
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
|
示例 2:
示例 3:
提示:
- 树中结点数在范围
[0, 2000] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:你可以使用原地算法(O(1) 额外空间)展开这棵树吗?
方法一
- 将左子树插入到右子树的地方
- 将原来的右子树接到左子树的最右边节点
- 考虑新的右子树的根节点,一直重复上边的过程,直到新的右子树为 null
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
1
\
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
1
\
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
1
\
2
\
3 4
\
5
\
6
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
......
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
} else {
TreeNode pre = root.left;
while (pre.right != null) {
pre = pre.right;
}
pre.right = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
}
|
方法二
反向后序遍历
因为右节点已经访问过,所以可以直接将每次访问的结点指向右节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class Solution {
private TreeNode pre = null;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
root.right = pre;
root.left = null;
pre = root;
}
}
|
