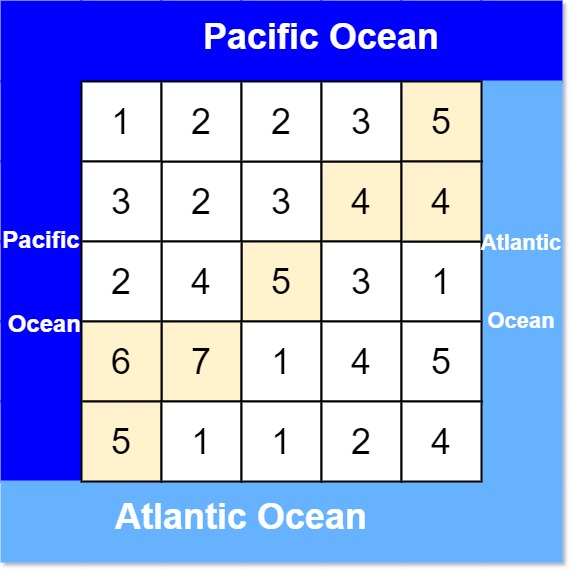
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回网格坐标 result 的 2D 列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水从单元格 (ri, ci) 流动 既可流向太平洋也可流向大西洋 。
示例 1:
示例 2:
1 2 输入: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]] [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
提示:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[r].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heights[r][c] <= 105
暴力解法:
遍历每个点,然后看这个点能不能同时到达太平洋和大西洋
使用DFS或BFS遍历要先判断下一个节点是否能到达,在进行遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();int [][] move = {{0 ,1 }, {0 ,-1 }, {1 ,0 }, {-1 ,0 }}; boolean [][] visited;public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic (int [][] heights) {new boolean [heights.length][heights[0 ].length];for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length; i++){for (int j = 0 ; j < heights[0 ].length; j++){if (isAns(heights, i, j, visited)){return ans;public boolean isAns (int [][] heights, int x, int y, boolean [][] visited) {boolean isPacific = false ;boolean isAtlantic = false ;new boolean [heights.length][heights[0 ].length];for (int i = 0 ; i < heights[0 ].length; i++){if (visited[0 ][i]) isPacific = true ;for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length; i++){if (visited[i][0 ]) isPacific = true ;for (int i = 0 ; i < heights[0 ].length; i++){if (visited[heights.length-1 ][i]) isAtlantic = true ;for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length; i++){if (visited[i][heights[0 ].length-1 ]) isAtlantic = true ; return isPacific && isAtlantic;public void dfs (int [][] heights, int x, int y, boolean [][] visited) {true ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){int next_x = x + move[i][0 ];int next_y = y + move[i][1 ];if (next_x < 0 || next_y < 0 || next_x >= heights.length || next_y >= heights[0 ].length || visited[next_x][next_y]){continue ;if (heights[next_x][next_y] <= heights[x][y]){
时间复杂度:$O(m^2 * n^2)$ :遍历每一个节点,是 m * n,遍历每一个节点的时候,都要做深搜,深搜的时间复杂度是: m * n,这是一个四次方的时间复杂度。
优化:
逆向思维,判断从太平洋或大西洋出发能到达哪些节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();int [][] move = {{0 ,1 }, {0 ,-1 }, {1 ,0 }, {-1 ,0 }}; boolean [][] isPacific;boolean [][] isAtlantic;public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic (int [][] heights) {int n = heights.length;int m = heights[0 ].length;new boolean [n][m];new boolean [n][m];for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){0 , i, isPacific); 1 , i, isAtlantic); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){0 , isPacific); 1 , isAtlantic); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++){if (isPacific[i][j] && isAtlantic[i][j]){return ans;public void dfs (int [][] heights, int x, int y, boolean [][] visited) {true ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){int next_x = x + move[i][0 ];int next_y = y + move[i][1 ];if (next_x < 0 || next_y < 0 || next_x >= heights.length || next_y >= heights[0 ].length || visited[next_x][next_y]){continue ;if (heights[next_x][next_y] >= heights[x][y]){
时间复杂度:$O(2m n)$,因为地图中每个节点最多只会遍历2遍