给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
1
2
3
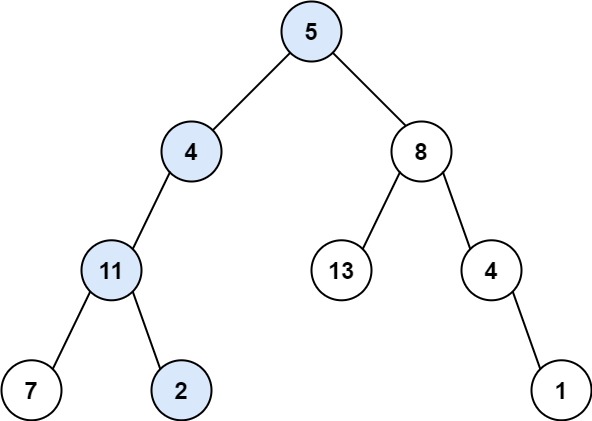
| 输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
|
示例 2:

1
2
3
4
5
6
| 输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:false
解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径:
(1
(1
不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
|
示例 3:
1
2
3
| 输入:root = [], targetSum = 0
输出:false
解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
|
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
迭代(后序遍历)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while(root != null || !st.isEmpty()){
while(root != null){
st.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = st.peek();
if(root.right == null || pre == root.right){
if(root.left == null && root.right ==null){
int pathSum = 0;
for(TreeNode node : st){
pathSum += node.val;
}
if(pathSum == targetSum){
return true;
}
}
root = st.pop();
pre = root;
root = null;
}else{
root = root.right;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
回溯
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
int pathSum = 0;
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
return has_sum(root,targetSum);
}
public boolean has_sum(TreeNode root,int targetSum){
if(root==null) return false;
pathSum += root.val;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
if(pathSum==targetSum){
return true;
}
}
if(root.left!=null){
if(has_sum(root.left,targetSum)) return true;
pathSum -= root.left.val;
}
if(root.right!=null){
if(has_sum(root.right,targetSum)) return true;
pathSum -= root.right.val;
}
return false;
}
}
|

