你会得到一个字符串 s (索引从 0 开始),你必须对它执行 k 个替换操作。替换操作以三个长度均为 k 的并行数组给出:indices, sources, targets。
要完成第 i 个替换操作:
- 检查 子字符串
sources[i] 是否出现在 原字符串 s 的索引 indices[i] 处。
- 如果没有出现, 什么也不做 。
- 如果出现,则用
targets[i] 替换 该子字符串。
例如,如果 s = "abcd" , indices[i] = 0 , sources[i] = "ab", targets[i] = "eee" ,那么替换的结果将是 "eeecd" 。
所有替换操作必须 同时 发生,这意味着替换操作不应该影响彼此的索引。测试用例保证元素间不会重叠 。
- 例如,一个
s = "abc" , indices = [0,1] , sources = ["ab","bc"] 的测试用例将不会生成,因为 "ab" 和 "bc" 替换重叠。
在对 s 执行所有替换操作后返回 结果字符串 。
子字符串 是字符串中连续的字符序列。
示例 1:

1
2
3
4
5
| 输入:s = "abcd", indices = [0,2], sources = ["a","cd"], targets = ["eee","ffff"]
输出:"eeebffff"
解释:
"a" 从 s 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。
"cd" 从 s 中的索引 2 开始,所以它被替换为 "ffff"。
|
示例 2: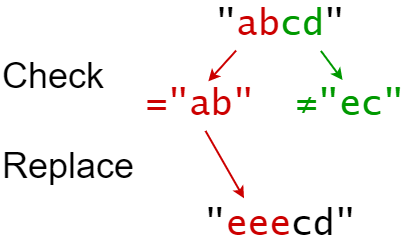
1
2
3
4
5
| 输入:s = "abcd", indices = [0,2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"]
输出:"eeecd"
解释:
"ab" 从 s 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。
"ec" 没有从原始的 S 中的索引 2 开始,所以它没有被替换。
|
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indices[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50s 仅由小写英文字母组成sources[i] 和 targets[i] 仅由小写英文字母组成
代码
模拟
先按照下标从小到大排序
可以用一个集合来保存下标的顺序
通过遍历已排好序的下标完成对字符串的查找与替换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public String findReplaceString(String s, int[] indices, String[] sources, String[] targets) {
int len = indices.length;
List<Integer> seq = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
seq.add(i);
}
Collections.sort(seq,(i,j)->indices[i]-indices[j]);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
int pluslen = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int j = seq.get(i);
int index = indices[j];
int sublen = sources[j].length();
if(index + sublen > s.length()){
continue;
}else{
String substr = s.substring(index, index + sublen);
if(substr.equals(sources[j])){
sb.replace(pluslen + index, pluslen + index + sublen, targets[j]);
pluslen += targets[j].length() - substr.length();
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
|

